What is Corporate Accounting?
The branch of accounting that is in charge of preparing and consolidating the company’s general ledgers and financial statements is corporate accounting.
Corporate accounting deals with accounting a company’s finances using private accountants hired by the business. It keeps track of all the day-to-day expenses incurred by the company, including its income statements, financial accounts, cash flow statements, etc.
[ez-toc]
Unlike traditional accountants, corporate accountants work on a single company’s finances rather than a wide range of clients. They develop a thorough knowledge of the company’s financial reports and performance to gain expertise. Their accounting services include:
- Preparing and managing accounts
- Analyzing financial reporting to facilitate decision-making
- Researching and keeping the board informed of a potential financial decision
- Overseeing accounting procedures and transactions to ensure compliance with the applicable rules and regulations
- Consolidating balance sheets regularly
- Creating financial and income flow statements
- Assessing internal controls, including risk assessments
This role of a corporate accountant has become indispensable for a company or business. Keeping accounts and financial statements up-to-date and accurate is important for legal reasons, in case of official audits, applying for loans, or declaring bankruptcy.
Otherwise, external audits can easily flag a business for not meeting U.S. auditing standards, such as the flagging of the five huge companies in March 2022.
Importance of Corporate Accounting
Every company or business registered with the government needs corporate accountants to take care of the legal, financial, and operational issues and provide expert inputs.
The financial scandals that emerged in the early 2000s were due to poor accounts management and a lack of corporate accounting. The industry’s ten names fell to bankruptcy due to huge accounting loopholes. This highlights the importance of corporate accountants for a company.
Here is a breakdown of the objectives of corporate accounting and how important it is for a company’s survival and smooth operation:
- Corporate accounting keeps a record of transactions systematically so that every transaction is known and documented. These records are then secured permanently in the accounting ledger to be accurately available for legal proceedings, analysis, and financial audits.
- The net appreciation of profit and loss can be ascertained through the regular preparation of income statements. This greatly helps with cash flow management, which is crucial for the survival of a business or company.
82% of all businesses fail because of poor cash flow management. 99.7% of these are small business owners, and only 30% of them prioritize corporate accountants. Also, 60% of these business owners believe they do not have enough accounting knowledge and understanding. You can see why so many businesses fail every year and how important corporate accounting is for a company. - As part of corporate accounting, balance sheets ascertain assets and liabilities of concern at a particular date. This way, corporate accountants keep the stakeholders informed of their financial position and help them make better management decisions.
- Corporate accounting results and reports play a key role in determining and evaluating management policy. If a certain operation or production continues to reap losses, the management decides to put it in the backseat. And financial statements provide the necessary statistics for making such decisions.
- An in-house accountant or accounting team ensures accountability among the managers of various departments. This prevents money defalcation, misappropriation of cost control, and major errors in data input by ensuring transparency.
- Efficient corporate accounting regularly tests the arithmetic accuracy of the account balances. It involves preparing a trial balance sheet with the inputs of credit, debit, and account titles. When the trial balance agrees, it confirms that the accounts are arithmetically accurate and up-to-date.
- Laws such as the Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX) require public and non-public companies to keep secure and safeguard financial records and destroy them in certain situations to prevent criminal access. Corporate accounting also ensures a company’s compliance with all these laws and regulations.
Differences: Corporate Accounting vs. Financial Accounting vs. Public Accounting
| Corporate Accounting | Financial Accounting | Public Accounting |
| Corporate accounting refers to handling the accounts of a single company or working for a single employer. These are salary-employed accountants with private accounting job responsibilities. | Financial accountants work independently or with an accounting firm. They do not have a single employer, although the firm may hire accountants on salary. But mostly, financial accountants work with various clients and projects. | Public accounting deals with several clients and companies. Usually, these are associated with government agencies and jobs. |
| Corporate accounting job responsibilities include handling all accounting tasks in a private business, internal controls, payroll and expense management, budget planning, etc. | Their job description mainly involves contract-based tasks such as creating financial reports, conducting internal audits, providing financial analysis, and facilitating data-driven business decisions. | Public accountants review financial documents before public disclosure. Government agencies, they perform financial audits for the government, investigate money frauds, and manage public funds. |
| Private accounting does not have to adhere to national and international accounting standards. The standards of the hiring company apply only. | Financial accountants only follow the current accounting standards applied by the U.S. government. The accounting standards of the client’s company do not apply. | Public accountants receive instructions from the government for public disclosure tasks and public Fund management, so their standards are also universal. |
| Corporate accountants may or may not take additional private clients depending on the terms and conditions of their contracts. | Financial accountants are not bound to limit their clients. They can take up any number of company audits and accounting projects. | Public accountants cannot take private clients. They are hired by government departments such as the IRS, which binds their accounting services. |
What is the Role of a Corporate Accountant?
The role of corporate accountants is multi-dimensional and crucial to the smooth operation of a business. Corporate accountants help a company or business run seamlessly in the following ways:
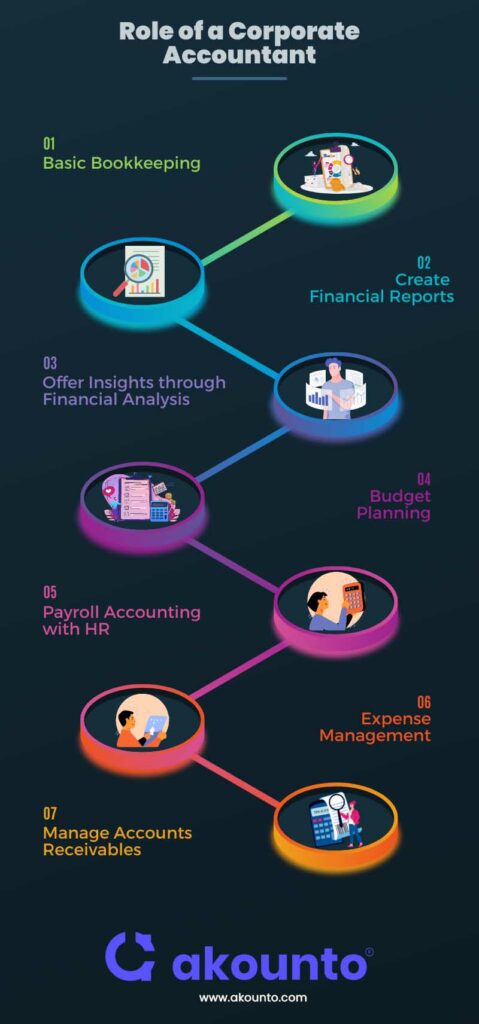
1. Basic Bookkeeping
Entry-level accountants keep a record of financial transactions and prepare source documents for business operations. But the role of a corporate accountant here is to supervise the team and ensure that the basic bookkeeping is up-to-date.
2. Create Financial Reports
The most important role of a corporate accountant is to create financial reports such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets. These financial statements represent a company’s current financial activity and position and help data-driven business decisions and operations.
3. Offer Insights through Financial Analysis
The in-house corporate accounting department, supervised by a chief financial officer, provides informed insights through financial analyses and comparisons to help decide whether a business decision is profitable. So, interpretation of the financial results and their comparison with the market are important responsibilities of a corporate accountant.
4. Budget Planning
Accountants associated with a company are also responsible for allocating a budget and creating spending and profit goals that align with the company’s financial situation. Corporate accountants run audits and checks to make sure the departments stick to the allocated budget and spending goals.
5. Payroll Accounting with HR
Large companies have human resources departments to handle basic staff salaries, retirement accounts, and other payroll-related tasks. The role of a corporate accountant remains because he has to tabulate this data, analyze it against the company revenue, and calculate employee taxes and bonuses.
HR and corporate accounting complement each other in this case.
6. Expense Management
All company departments send their expense requests to the corporate accountant, and invoice processing is also the responsibility of the company’s accountant. The accountant then approves or rejects invoices and requests considering the company’s account balance, revenue, and financial performance.
7. Manage Accounts Receivables
For small to medium-sized businesses, the role of a corporate accountant also includes keeping track of the accounts receivables. They work up the past due payments of the company, get in contact with the collection agents, and bring them in to improve the cash flow.
Find out how Akounto can help you in Corporate Accounting and all the tasks related to it for better account management and financial reporting.
Get started today and find out all the information that you need for your company’s accounting solutions.