What is Negative Cash Flow?
Negative cash flow occurs when a business’s cash outflows exceed its cash inflows, potentially leading to financial challenges.
Negative cash flow is a financial situation in which a company’s cash expenses exceed the cash generated from its operations, investments, and financing activities during a specific period, as reflected in its cash flow statement.
What’s covered in the article
In contrast, positive cash flow refers to a situation where a business has more cash inflow than outflows for a given period leaving more money with the company.
When a business experience negative cash flow, it could be difficult to meet its financial obligations and cover expenses such as paying employees, suppliers, or debtors, leading to insolvency if not addressed promptly.
Cash Flow Statements and Negative Cash Flow
Negative cash flow can be observed and analyzed through the cash flow statement, which breaks down cash inflows and outflows into three main categories: operating, investing, and financing activities.
If a business experiences negative cash flow from its operating activities, it is not generating enough cash from its core operations to cover its expenses. This could indicate poor operational efficiency or financial management.
Negative cash flow from investing activities usually results from the company investing in assets, such as equipment, property, or other long-term investments, to expand or improve its business. This negative cash flow may not be as concerning as it could lead to future growth and higher positive cash flows.
Negative cash flow from financing activities arises when a company pays off debts, pays dividends, or repurchases its shares, indicating that the company is financially stable enough to return value to its shareholders or reduce its debt burden.
General Causes of Negative Cash Flows for a Small Business
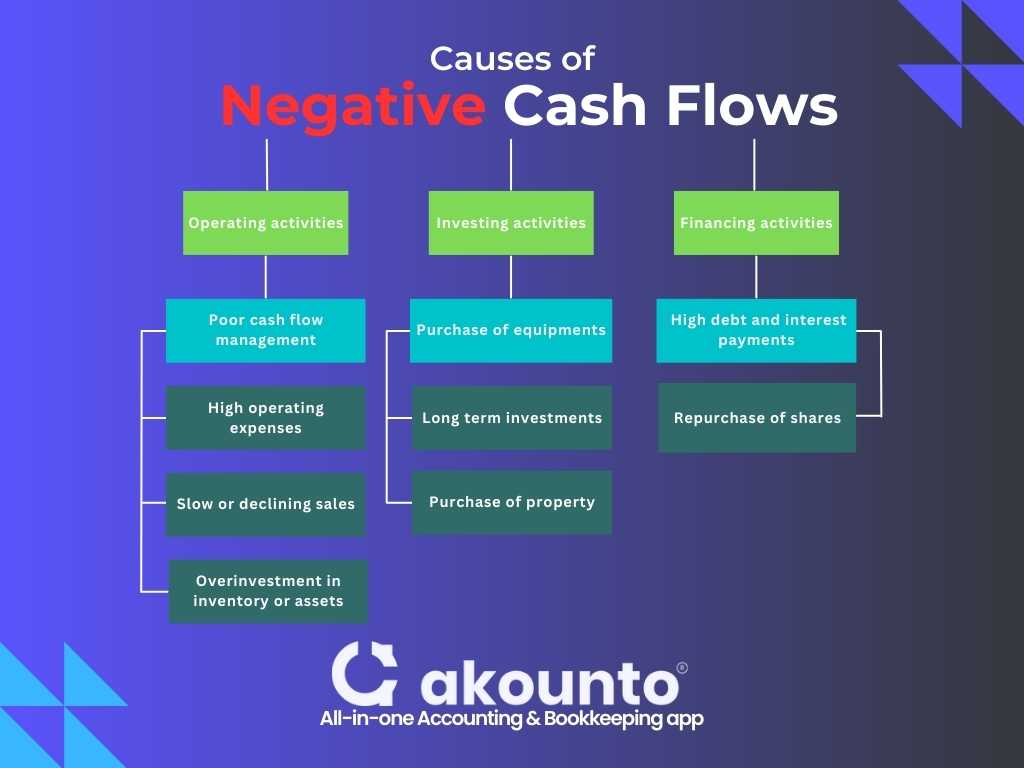
- Poor cash flow management: Inefficient tracking and management of cash inflow and outflow may result in a negative cash flow. Small businesses must monitor their cash flow closely, using tools like cash flow forecasts to anticipate and mitigate potential cash shortfalls.
- High operating expenses: Elevated operating costs can contribute to negative cash flow, particularly if a business’s revenue cannot cover its expenses. Companies must control their operating expenses and explore cost-saving measures.Adverse operating cash flow signifies inefficient business operations leaving the scope to optimize production processes and other routine operations.
- Slow or declining sales: A decline in sales or slow-paying customers can lead to reduced incoming cash, resulting in negative cash flow. Companies must continually evaluate their sales performance, implement strategies to boost revenue and ensure timely collection of receivables.
- Overinvestment in inventory or assets: Excessive investment in inventory or other assets can tie up a company’s cash, leading to negative cash flow. Optimizing inventory levels and making prudent decisions regarding asset purchases are essential.
- High debt and interest payments: Businesses with substantial debt may face negative cash flow due to high-interest payments and principal repayments. Reducing debt and managing borrowing costs can help mitigate the impact of debt on cash flow.
By understanding the causes and sources of negative cash flow, businesses can take appropriate action to address these issues and work towards achieving a positive cash flow.
Impacts of Negative Cash Flow
When a business is experiencing negative cash flow, the following scenarios threaten its solvency and liquidity position:
- Difficulty meeting financial obligations: When a business’s cash outflows exceed its outgoing cash, it may struggle to pay employees, suppliers, and creditors on time. This can harm the company’s reputation, relationships, and creditworthiness, eventually impacting business growth.
- Limited growth potential: Negative cash flow restricts a business’s ability to invest in expansion, marketing, research, and development, or other growth-driving activities, potentially stunting its long-term potential.
- Reduced access to financing: Lenders and investors may be reluctant to provide financing to businesses with persistent negative cash flow, which could signal instability in the business’s financial health.
- Increased risk of insolvency: In the worst-case scenario, ongoing negative cash flow can lead to insolvency, where a company cannot pay its debts and may be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation.
Managing Negative Cash Flow
Improve Cash Flow Forecasting
Cash flow forecasting is a crucial aspect of managing your business’s finances. By creating a cash flow forecast, you can anticipate future inflows and outflows, helping a small business owner to identify possible cash flow problems proactively.
Regularly updating your cash flow forecast will enable you to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to maintain a healthy cash flow.
For small business owners, cash flow forecasting can be the key to staying ahead of financial challenges and ensuring business sustainability.
Enhance Accounts Receivable Management
Implement policies to expedite customer payment, such as offering early discounts, establishing clear payment terms, and consistently following up on overdue invoices.
Receivables management is important as it reflects the efficiency of the working capital cycle and the ability to convert credit sales into incoming cash.
Optimize Inventory Management
Streamline inventory levels to reduce carrying costs and avoid tying up cash in unsold products. Implement efficient inventory management systems and consider just-in-time inventory management to minimize stock levels.
Small businesses must cover supplier payments to avoid defaults when there is a cash flow deficit.
Reduce Operating Expenses
Identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses, renegotiate contracts with suppliers, and explore cost-saving opportunities to lower operating costs and alleviate pressure on cash flow.
Make provisions for unexpected expenses and monitor overhead costs. A business owner must search for an affordable alternative for every cost center within the production process. Some solutions include optimizing a company’s operations by automating, outsourcing, lean inventory management, etc.
Restructure Debt
Debt restructuring is a proactive approach that can be used to manage negative cash flow and address financial challenges that arise in a business. It involves working with creditors to modify the terms of existing debts or consolidate debts into new loans with more favorable terms.
By doing so, a company can reduce its monthly cash outflow and improve its liquidity, which can help to support its day-to-day operations and future growth. A successful debt restructuring plan should be tailored to the unique needs of the business and take into account its current financial statement, projected cash flow, and future growth potential.
To be effective, debt restructuring should be approached strategically and with a clear understanding of the business’s financial situation. It is important to work with experienced financial professionals who can help develop a comprehensive financial plan that considers both short-term and long-term goals.
Increase Sales and Revenue
Develop strategies to boost sales, such as expanding marketing efforts, entering new markets, or introducing new products or services. The idea is to increase gross revenue or topline while taking advantage of the market situation and get maximum ROI to the extent possible.
When a company is generating more revenue, it has more money coming in, which can help to offset the cash going out and improve the overall financial position of the business.
Use an Accounting Software
Business owners should consider using accounting software or working with financial professionals to create and update cash flow projections, allowing them to make informed decisions and steer their businesses toward success.
Accurate forecasting allows business owners to anticipate potential cash shortfalls and implement strategies to mitigate their impact.
By revisiting and updating cash flow projections based on actual financial performance, businesses can identify trends and adjust their financial plans accordingly.
Can a Business Be Profitable with Negative Cash Flow?
Yes, a business can be profitable with negative cash flow, although this situation is often temporary and may arise for various reasons.
- A company’s earnings could be high, but poor timing of inflows and outgoing expenses might result in negative cash flow.
- Investing activities, such as purchasing equipment for expedited growth, can also lead to negative cash flow despite a business’s profitability.
Tips to Manage Negative Cash Flow
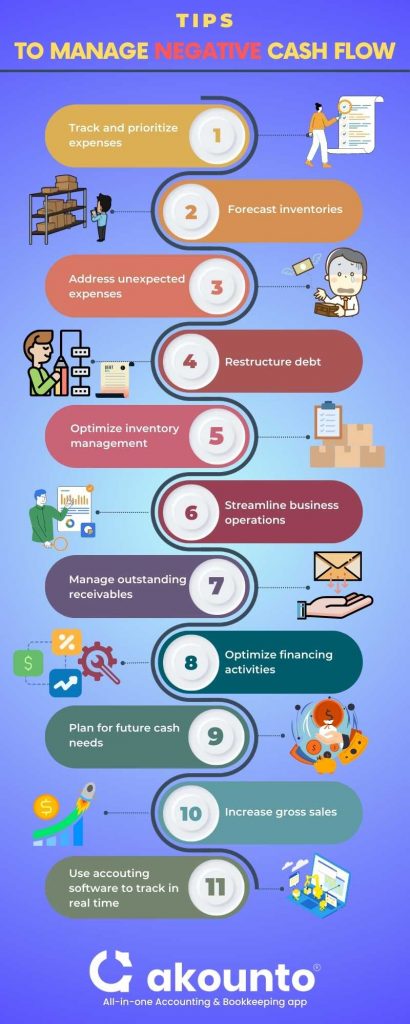
- Track and prioritize expenses: Monitor and prioritize all business expenses based on their importance. Allocate funds to cover essential costs like supplier payments, insurance premiums, and overhead costs first.
- Address unexpected expenses: Create an emergency budget for unforeseen expenses like equipment maintenance, legal fees, or insurance claims to prevent sudden cash outflows from disrupting operations.
- Streamline business operations: Identify areas of poor or inefficient operations and implement changes to increase efficiency and reduce costs, such as finding affordable alternatives or renegotiating contracts with suppliers.
- Manage outstanding receivables: Regularly review accounts receivable and implement strategies to encourage prompt payment, such as offering discounts for early payments or employing a collections agency.
- Optimize financing activities: Evaluate financing options, such as loans or lines of credit, to support business activities during periods of negative cash flow. Monitor interest rates and negotiate better terms if possible.
- Plan for future cash needs: Regularly assess the company’s financial plan and adjust it as needed to ensure there is enough cash to cover next month’s obligations, such as paying dividends, keeping operations afloat, and maintaining working capital.
By implementing these tips, small businesses can manage negative cash flow effectively and work towards maintaining a healthy financial position.
Conclusion
While negative cash flow can be concerning, it is essential to differentiate between temporary cash flow deficits and chronic cash flow issues.
By actively monitoring cash flow measures, optimizing business operations, and implementing financial planning, companies can experience net profit and achieve healthy cash flow despite short-term setbacks.
Sign-up with Akounto’s accounting software and get accurate and timely cash flow and other important financial statements.